The Power of Synthetic Customers
Discover the impact of synthetic customers on precision marketing strategies. Read our blog for valuable insights on synthetic customers.
October 6, 2025

Customer acquisition and retention are becoming increasingly challenging and expensive. Marketing leaders face constant pressure to show ROI and justify every marketing dollar.
But what if you could predict your customers’ next steps, refine campaigns before they launch, and deliver personalized experiences at scale?
This post explores how businesses can leverage synthetic customers to enhance marketing strategies, product development, and brand experiences.
What are synthetic customers and how are they created?
Synthetic customers are simulated profiles generated using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) that represent ideal customer segments based on market research and data analytics. Algorithms analyze anonymized and aggregated customer behavior, preferences, and demographics to create synthetic datasets for targeted marketing strategies.
These datasets mimic the statistical properties of real customer data containing no personally identifiable information.
Synthetic customers vs. customer personas
While both are research methods used to represent and understand audience segments, they differ significantly in their approach.
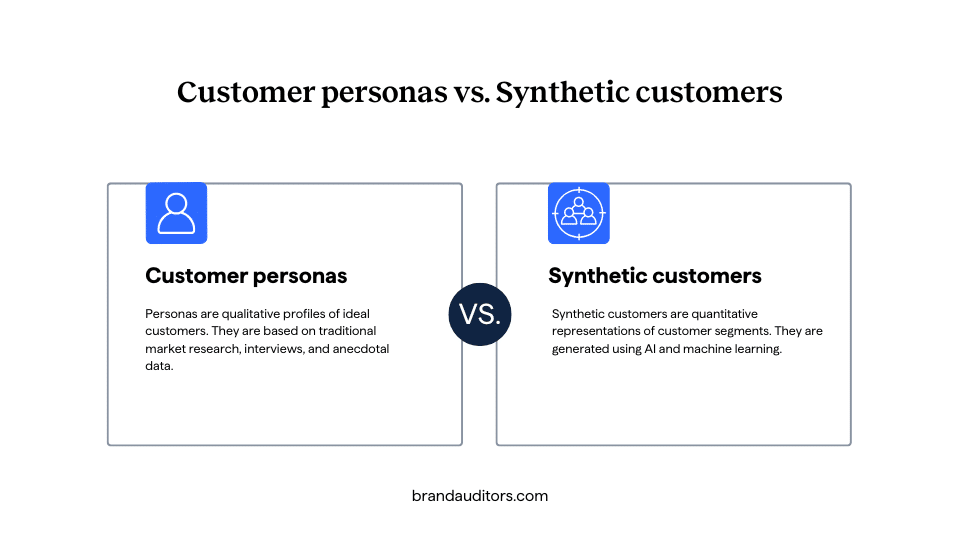
Customer personas
- Qualitative: Personas are qualitative profiles of ideal customers, often based on traditional market research, interviews, and anecdotal data.
- Subjective: Marketing teams typically create personas based on their own analysis of the target audience.
- Fictional: Personas are fictional characters with demographics, job titles, goals, pain points, and motivations. They often include a name and photo to represent a typical customer.
- Resource intensive: Developing and updating multiple detailed personas requires significant time and resources.
- Static: Personas need regular updates to reflect changes in the market or customer behavior.
Example: “Adventure-Seeking Alex,” a 35-year-old marketing professional who enjoys outdoor activities and seeks sustainable travel options.
Synthetic customers
- Quantitative: Synthetic customers are quantitative representations of customer segments.
- Data-driven: They are generated using AI and machine learning algorithms trained on anonymized and aggregated actual customer data.
- Statistical: Synthetic customers are statistical profiles that capture patterns and trends in consumer behavior, preferences, and demographics. They do not have individual names or photos.
- Efficient: Generating large numbers of synthetic customers is relatively easy and efficient.
- Dynamic: These models can be updated and refined as new data becomes available, enabling companies to adapt to evolving consumer needs and behaviors.
Example: A cluster of synthetic customers in urban areas who exhibit a high propensity to purchase organic food products online.
Which is better?
Personas and synthetic customers serve different purposes and complement each other effectively.
- Personas: Best used for communication and storytelling, conveying human emotions to make customer segments relatable and shaping marketing messages and creative work.
- Synthetic Customers: Provide more robust data analysis, testing, and modeling, offering a scalable way to understand customer behavior and create targeted marketing campaigns.
Companies often begin with personas to define customer segments and then use synthetic data to analyze those segments in greater detail. This data can also refine or validate existing personas.
Combining both approaches delivers the most comprehensive understanding of your target audience.
The business case for synthetic customers
Mid-sized and large companies need every advantage to thrive in today’s competitive market. Synthetic customer data empowers businesses to improve marketing strategies, increase ROI, and gain a competitive edge:
Deeper Customer Insights: Synthetic customers provide a granular understanding of customer preferences, behaviors, and motivations. These AI-generated profiles enable companies to identify patterns and trends within vast datasets that may be hidden in traditional analyses. This deeper understanding facilitates more targeted messaging and personalized offers.
Refine Campaigns with Accuracy: Companies can use synthetic customers to test and optimize marketing campaigns before launch. Simulating different scenarios and analyzing responses allows marketers to refine messaging, creative elements, and calls to action. Pre-launch testing minimizes wasted ad spend and ensures highly targeted and effective campaigns from the outset.
Building Personalized Customer Journeys: Synthetic customers simplify the creation of personalized customer journeys and user experiences. By understanding how different customer segments interact with various touchpoints, companies can optimize the customer journey at every stage. Personalization strengthens customer relationships, increases loyalty, and drives higher customer lifetime value (CLTV).
Accelerated Experimentation: Synthetic customers provide a risk-free environment for testing new ideas and marketing strategies rapidly. Companies can experiment with different approaches, messaging, and offers without impacting real customers, enabling rapid iteration, faster innovation, and improved campaign performance.
Reduced Time to Market: Companies can significantly reduce their time to market by using synthetic customers to test and refine campaigns before launch. This agility allows businesses to stay ahead of the competition and quickly adapt to changing market dynamics.

The drawbacks of using synthetic customers for marketing
While synthetic customers offer significant opportunities, they also present challenges. Businesses must consider these drawbacks to maintain effective and ethical strategies.
Data accuracy and reliability
The reliability of synthetic customers hinges on the quality of the AI/ML models and the input data. Flawed, biased, or incomplete input data will lead to inaccurate insights. For example, if a retail company builds personas based on historical data primarily focused on older demographics, it may overlook younger audiences. Such inaccuracies can result in poor decisions, wasted resources, and missed market opportunities.
Regular review of data sources and model refinement are crucial for minimizing errors and biases. It’s also important to acknowledge that synthetic data, while mimicking real data, can never perfectly replicate it.
Ethical concerns
Using synthetic customer data raises ethical considerations regarding privacy and consent. Even though the data isn’t directly tied to individuals, it often replicates the behaviors of real people based on analyzed data, blurring ethical lines and risking consumer trust.
For example, individuals might feel uneasy knowing companies closely simulate their behavior without explicit consent. Transparency and adherence to privacy laws like GDPR are essential to address these concerns and maintain trust.
Beyond privacy, ethical considerations should include the potential for manipulation or the creation of filter bubbles based on synthetic data.
Over-reliance on simulations
Synthetic customers are valuable for modeling behavior, but they cannot capture the full spectrum of human emotions and contextual factors that influence real-world decisions. Over-reliance on simulations can stifle creativity and lead to overly data-driven strategies that lack the human touch.
For instance, relying solely on synthetic personas might overlook cultural sensitivities or nuanced emotional motivations. Marketing teams should use synthetic customers as a powerful tool, but not as a replacement for real customer research, focus groups, and direct interactions.
Risk of misaligned strategies
Synthetic customers are only as effective as the data and assumptions behind them. If these digital personas don’t accurately represent the target audience, businesses risk developing poorly targeted marketing strategies. For example, campaigns successful in one region might fail in another because of cultural or regional differences.
Combining synthetic customer data with localized market research and real-world testing is essential to ensure strategies remain relevant and effective.
The Brand Auditors: Real-World Results with Synthetic Customers
At The Brand Auditors, we use synthetic customers to help our clients refine their brand and marketing strategies. Our focus is not just on creating artificial profiles, but on delivering actionable insights that translate into measurable business results.
For example, we partnered with a mid-sized regional construction company struggling to compete in a crowded market. Their marketing lacked focus and wasn’t resonating with different target audiences. We began by analyzing their ideal customers and the competitive landscape, identifying key customer segments and their unique needs.
Then, we applied our synthetic customer modeling, going beyond basic demographics to incorporate psychographic data like values, motivations, and online behavior. Our AI models uncovered crucial emotional drivers, such as the need for transparent pricing and clear timelines, as well as anxieties about the home construction process.
Armed with these insights, the company developed more targeted campaigns. Instead of generic messaging, they addressed specific customer concerns by offering solutions like detailed budget breakdowns, clear project timelines, and personalized communication. This resulted in significantly higher customer engagement and satisfaction. Specifically, we saw an increase in website traffic from targeted campaigns and a improvement in lead conversion rates.
Beyond improving marketing performance, the company confidently expanded into a new market, equipped with data-driven insights into the needs and preferences of customers in that region.
Our Unique Approach to Synthetic Customer Development
Our process begins with a comprehensive data analysis phase. We gather and anonymize data from diverse sources, including CRM systems, market research, and publicly available datasets. This data fuels our advanced AI models, designed to uncover complex relationships between demographics, psychographics, and online behaviors.
We incorporate behavioral modeling into our process. Rather than simply generating statistical averages, our AI simulates how various factors interact to influence customer decision-making. This allows us to create realistic profiles that capture not just what customers do, but why they do it.
The result is a set of rich, data-driven personas that provide a deeper understanding of each customer segment, helping our clients connect with customers on a more personal level. This leads to more targeted marketing strategies, personalized messaging, stronger customer relationships, and ultimately, higher ROI.
How synthetic customers are driving innovation across industries
While often used for targeted advertising and personalized experiences, synthetic customers have applications far beyond that, driving innovation and improving decision-making in various sectors.
Financial services: Understanding customer needs and mitigating risk
Synthetic customers are transforming how financial institutions operate:
- Personalized financial products: Banks can leverage synthetic customer profiles to develop and offer customized financial products, increasing customer satisfaction and driving revenue growth. For example, a bank could use synthetic customer data to simulate how different demographics might respond to a new mortgage product with variable interest rates. This allows them to optimize the product’s features and marketing. (Source: “Synthetic Data in Finance” – K2view)
- Credit risk assessment: Synthetic customer data can train credit scoring models, improving accuracy and reducing bias. Lenders can create more fair and inclusive lending practices based on synthetic data that reflects diverse populations and mitigates historical biases present in real-world data. (Source: “Synthetic Data: The Future of Data Sharing and Collaboration” – Data Ethics)
Healthcare: Improving patient care and accelerating research
The healthcare industry also benefits from synthetic patients:
- Personalized medicine: Synthetic patient data allows healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans based on individual patient characteristics, leading to more effective and targeted therapies. For instance, synthetic data could model the effectiveness of different drug dosages for patients with varying genetic predispositions. (Source: “Synthetic Data in Healthcare” – K2view)
- Clinical trial design: Synthetic patient data can simulate clinical trial scenarios, optimizing trial design and reducing the need for large-scale human trials. As a result, the organization can accelerate the development of new treatments and reduce costs. Researchers can use synthetic data to explore different trial parameters and predict their impact on the trial’s success rate. (Source: “Synthetic Data Use Cases for Every Company” – K2view)
Retail and e-commerce: Enhancing customer experience and driving sales
In the competitive retail landscape, understanding customer behavior is crucial:
- Personalized recommendations: Online retailers use synthetic customer data to provide more relevant and personalized product recommendations, increasing sales and customer engagement. By analyzing synthetic customer purchase patterns, retailers can recommend products that are frequently bought together or that align with individual customer preferences. (Note: While numerous articles discuss AI-powered recommendations, the direct link to synthetic customer data for this purpose is often less explicit. The connection is logical: synthetic data allows for training AI models without privacy concerns.)
- Market research and product development: Synthetic customer data helps simulate market trends and predict how different customer segments will respond to new products. This is invaluable for product development and market entry strategies. For example, a clothing retailer could use synthetic data to predict the demand for a new clothing line based on the preferences of different customer segments. (Source: “Are Synthetic Personas the New Normal of User Research?” – Delve AI)
Manufacturing: Optimizing processes and improving quality
Synthetic data can train predictive maintenance models, allowing manufacturers to anticipate equipment failures and optimize maintenance schedules. This reduces downtime and improves operational efficiency.
While not directly related to customers, it illustrates how synthetic data can represent complex systems and behaviors. For example, synthetic data could simulate the performance of a manufacturing machine under different operating conditions. So, manufacturers could identify potential points of failure and optimize maintenance schedules.
Are you prepared for the future of marketing with synthetic customers?
The use of synthetic customers and data for branding and marketing is rapidly evolving. As AI and machine learning technologies advance, we will see even more innovative applications across various industries.
This innovative technique is transforming how marketers understand and engage with their audiences. They help businesses make smarter, data-driven decisions, improve marketing efficiency, and boost ROI.
Are you ready to unlock the power of synthetic customers for your business? Connect with us to learn more about how we can help you drive marketing ROI and gain a competitive edge.
Ready to learn more?
Connect with a strategist for a no-obligation session designed to pinpoint your brand's biggest opportunities and get a clear path to successful outcomes.

POST AUTHOR
Core services
Digital marketing
audit services
Discover how to improve marketing campaigns, strengthen the impact of every customer touchpoint, and focus resources on the actions that generate more revenue.
Customer experience strategy consulting
Turn raw customer data into audience personas and laser-focused messaging.
